|
This web page is prepared for providing research materials of our spatially efficient annotated metro map project. |
Travel Guide Maps
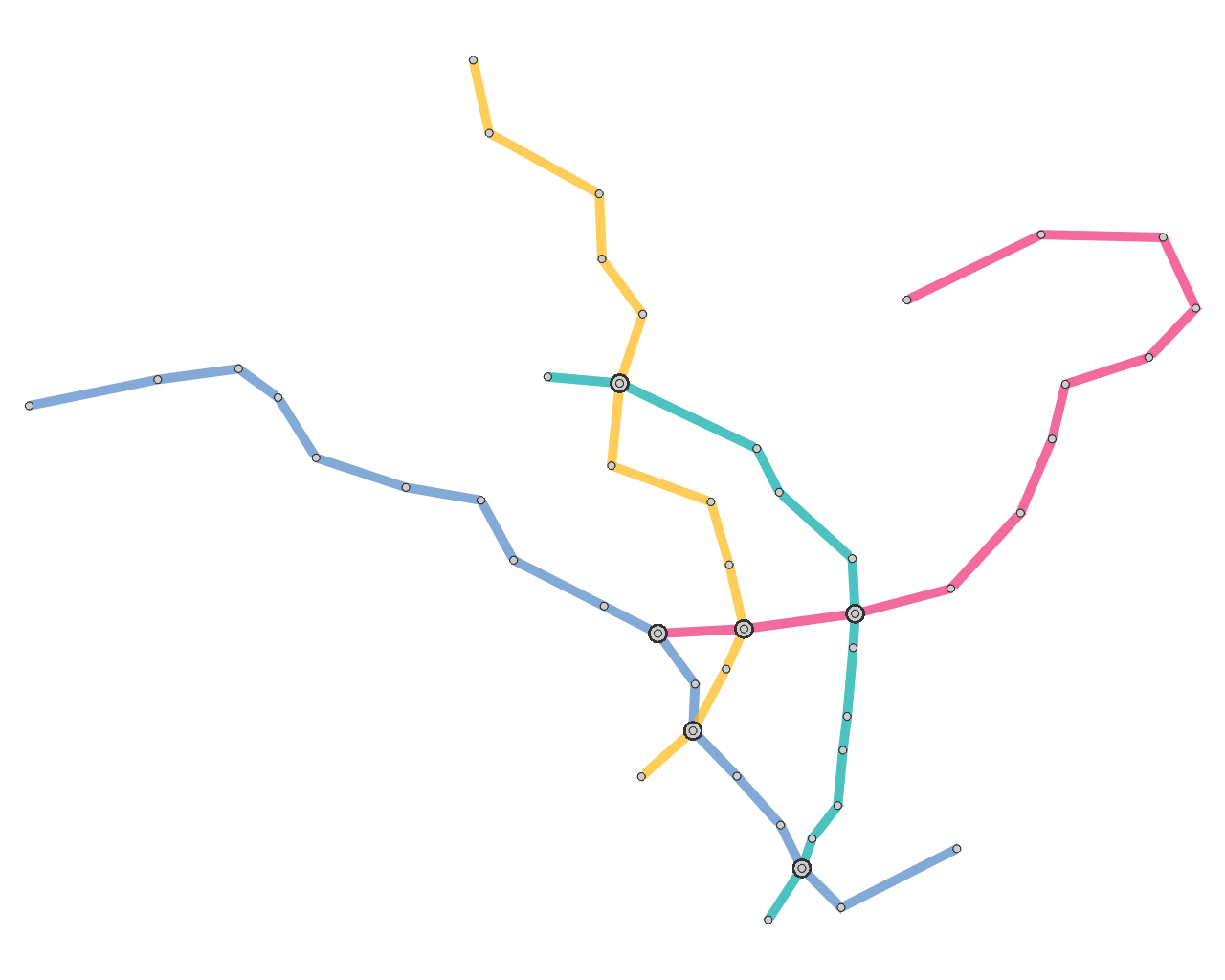
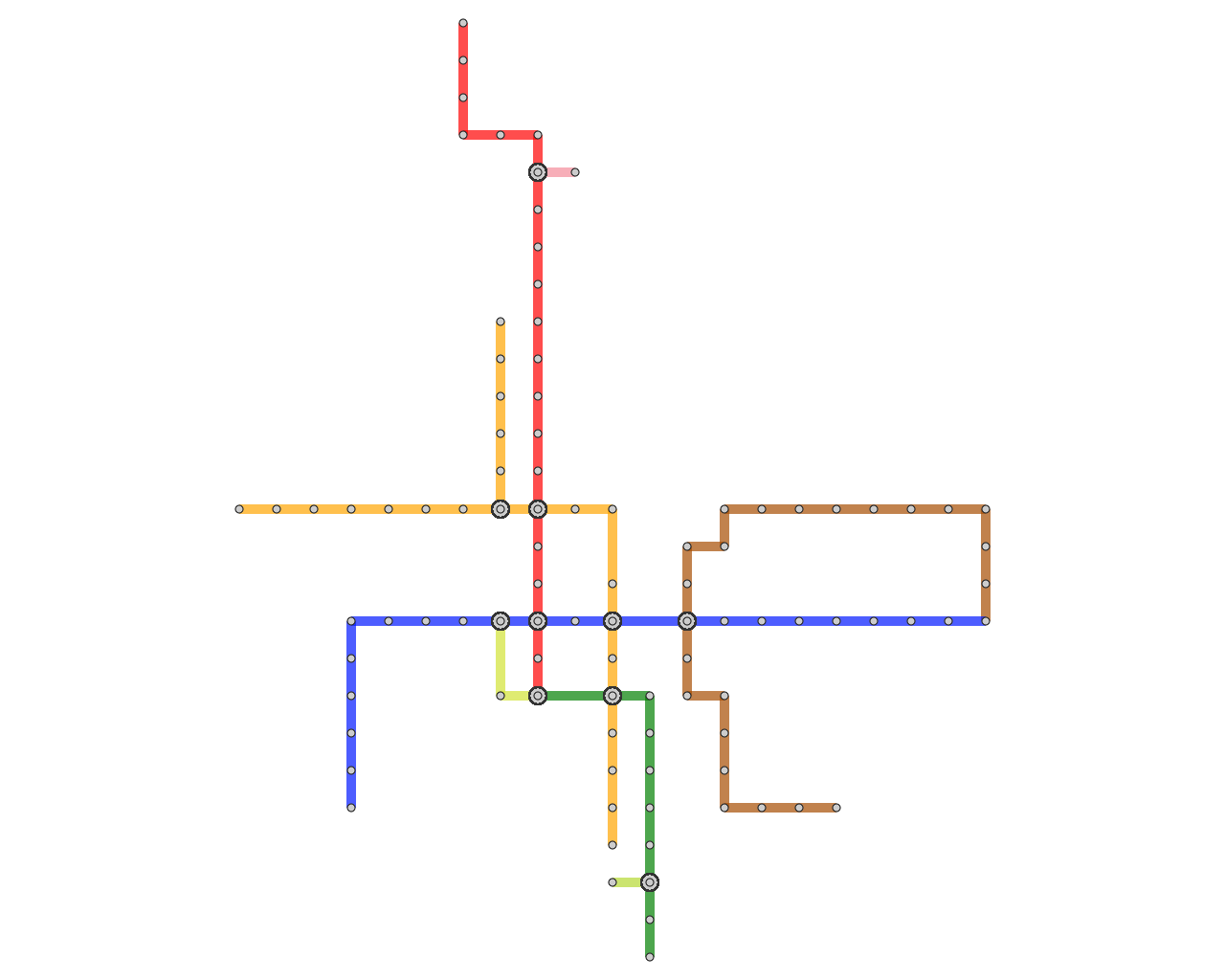
Schematic representation of metro maps significantly improves
the visual readability of the map contents due to its clear and
simplified layout design, especially for guiding complicated metro
networks. Currently available metro maps usually follow the
aesthetic criteria invented by Beck, where the metro lines
are aligned to horizontal and vertical directions and optionally 45
degree diagonal directions. In addition, annotating the map with
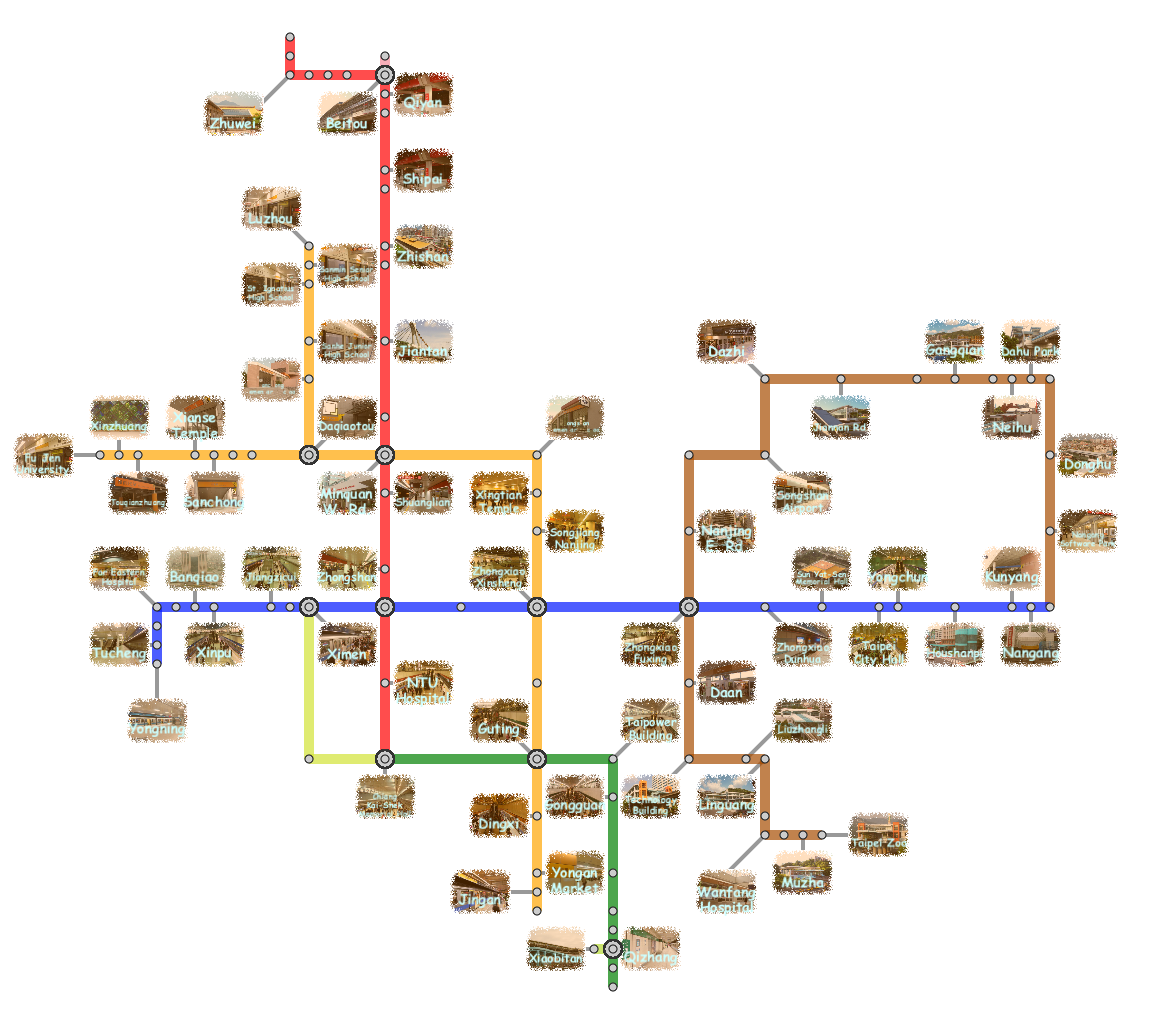
comprehensive explanations and photographs effectively allows us to
find sufficient information on our own places of interest. Actually,
this type of schematic representation with such large annotation
labels has been widely employed in commercially available metro
maps and travel guidebooks.
In this project, we present a new approach for designing the annotated
metro maps in order to distribute such labels in a well-balanced manner
to labeling regions around the metro network.
Then, we adjust the lengths of metro line and leader line segments, which
allows us to fully maximize the space coverage of the entire annotated map.
|
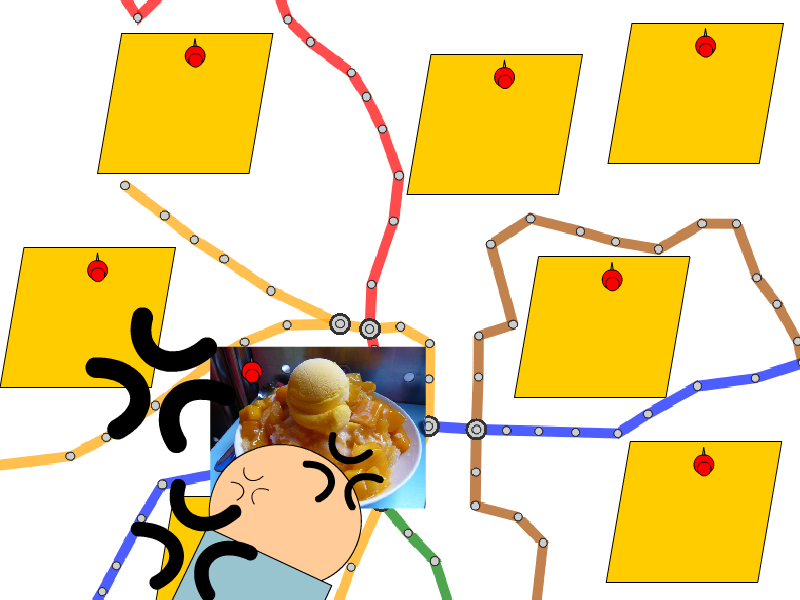
|
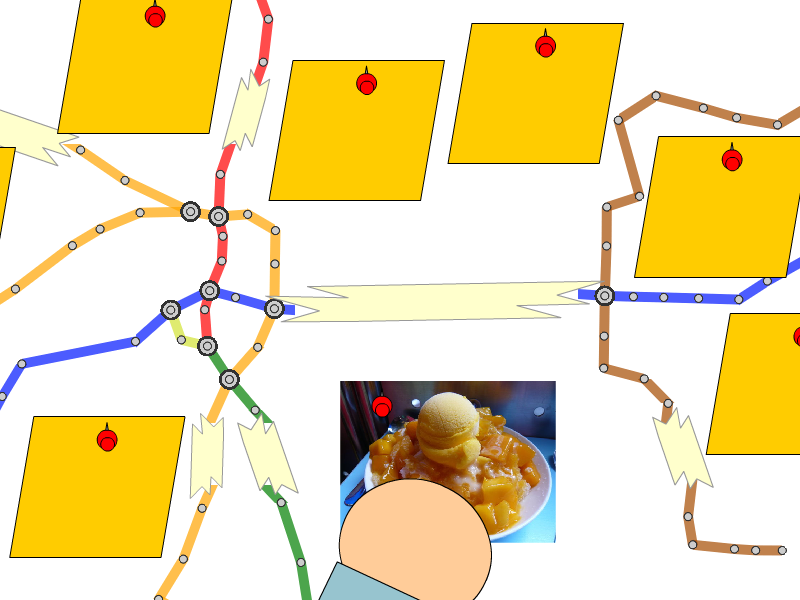 |
| (a) Less space for label placement | (b) Optimized annotated maps with rearranged layout |
|
Major criteria for designing schematic layout of the metro
network were intensively explored, while, for placing annotation
labels, only small textural labels such as station names
have been considered so far. However, map annotation with
large labels has been already popular among commercially
available travel guidebooks since they can assist travelers
with rich information about areas of interest. Unfortunately,
such maps have been manually composed by professional illustrators
only, due to the difficulty in finding visually appealing layout of large annotation labels.
In this project, we investigate important criteria for placing large
annotation labels to construct an automatic algorithm for
generating aesthetic annotated metro maps. Actually, by
studying common design rules employed in published guidebooks,
we formulate the following criteria as hard and soft constraints.
|
Hard Constraints |
Soft Constraints |
|
|
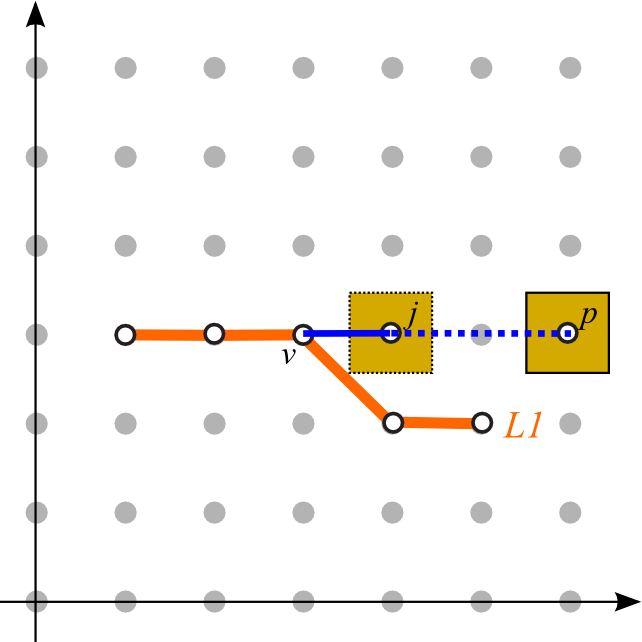 |
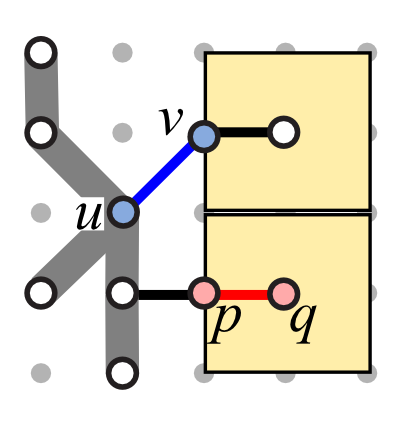
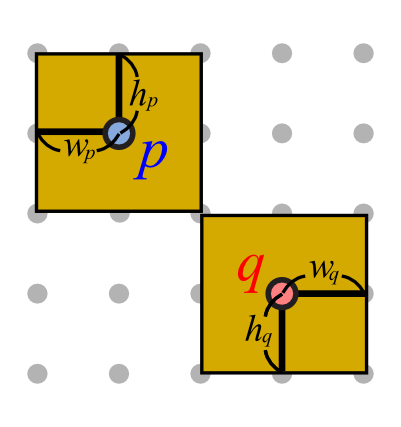
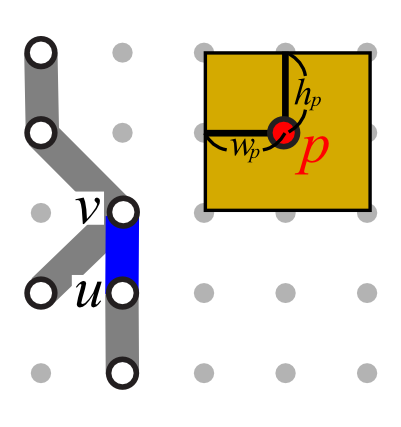
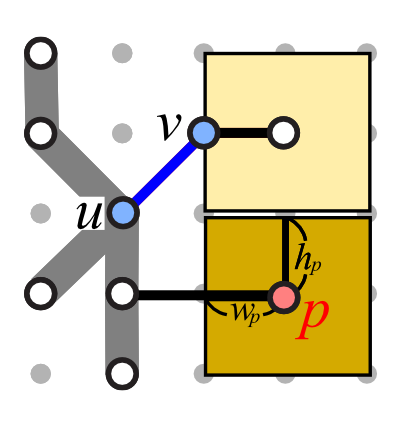
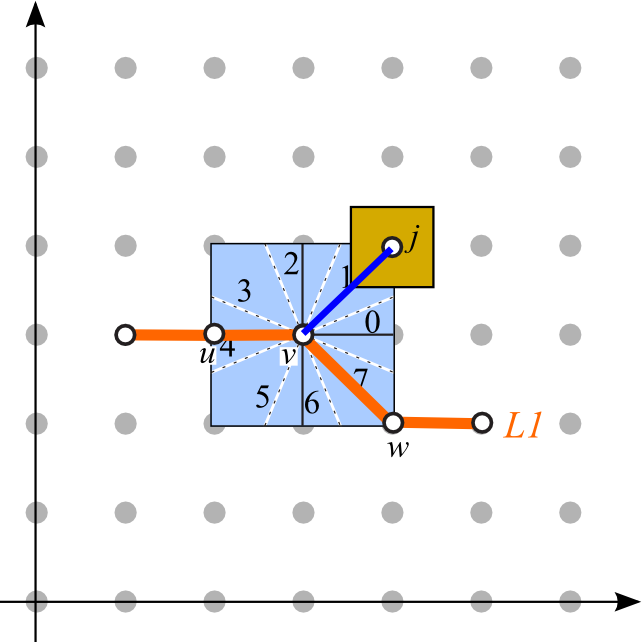
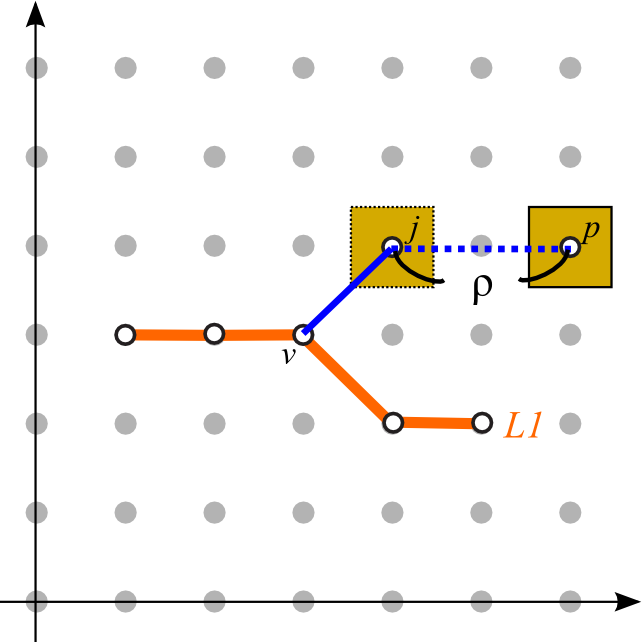
| (AS1) Leader orientation | (AS2) Total leader length | (AS3) Leader bends |

|

|
| (AS4) Closed regions | (AS5) Alternating distribution |
|
Note that the first two are formulated as hard constraints
while the last five are as soft constraints. In our approach,
we introduce these as additional constraints into the conventional
MIP formulation, so that we can seek a
reasonable compromise between the aesthetic layout of the
metro network and large annotation labels.
|
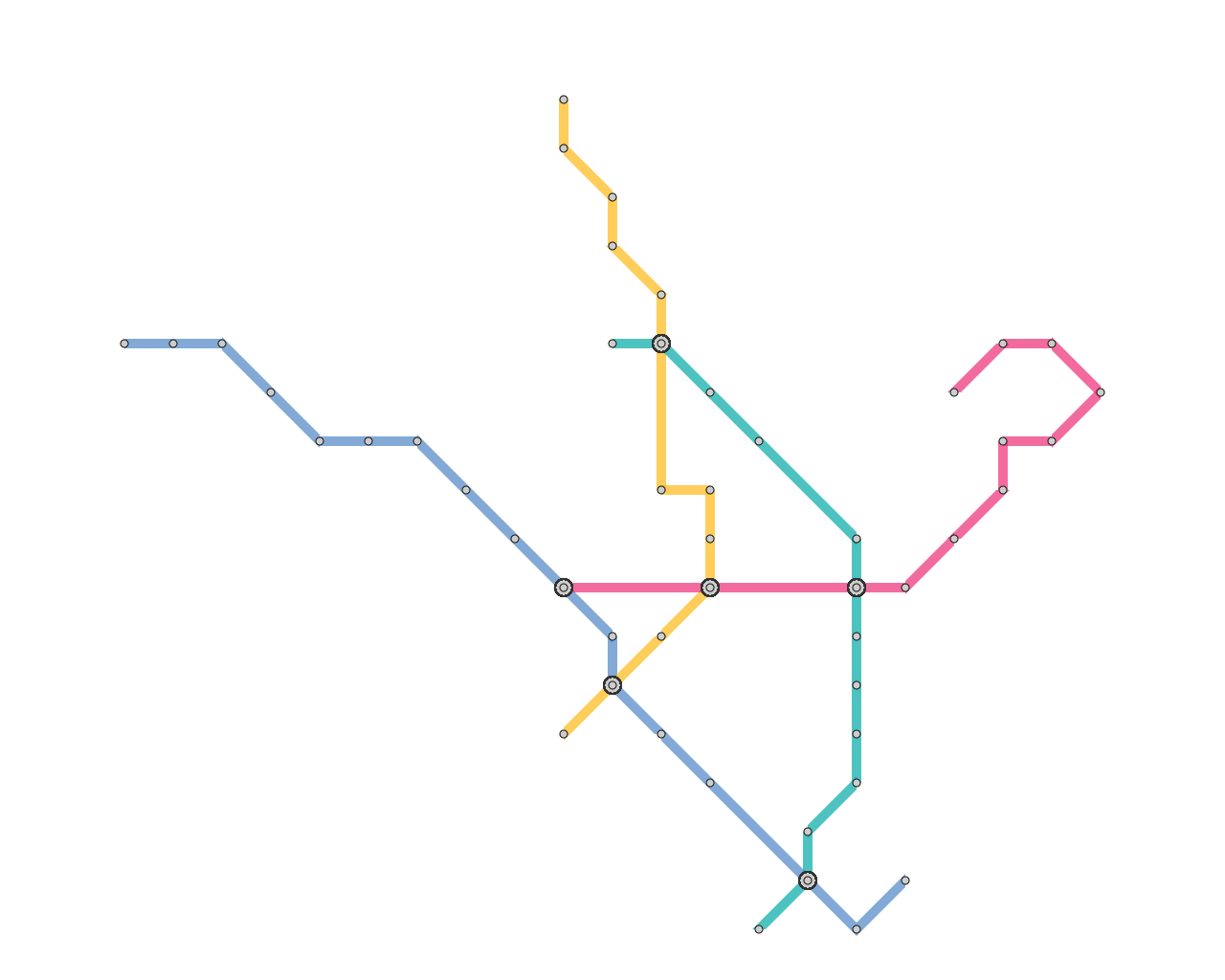
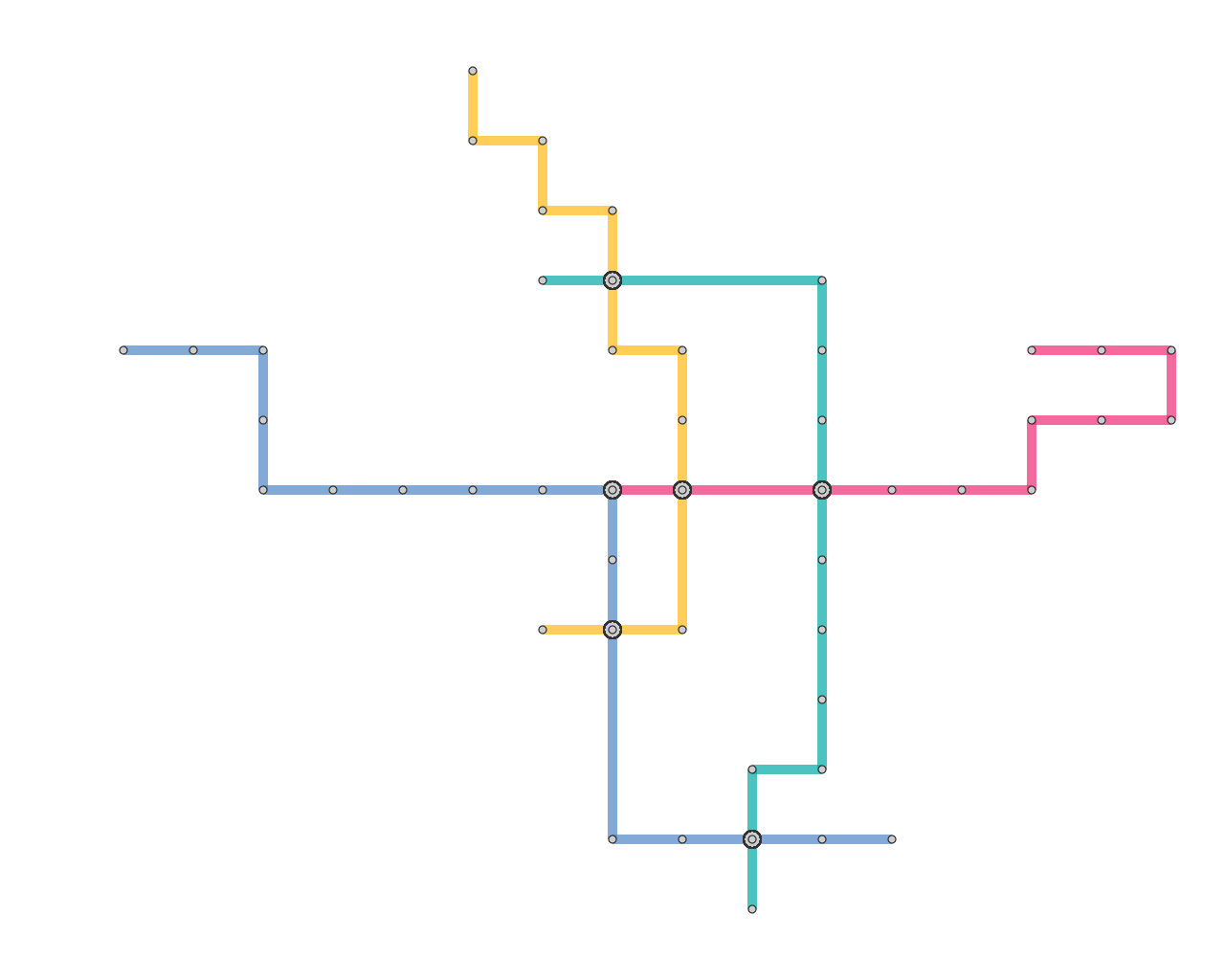
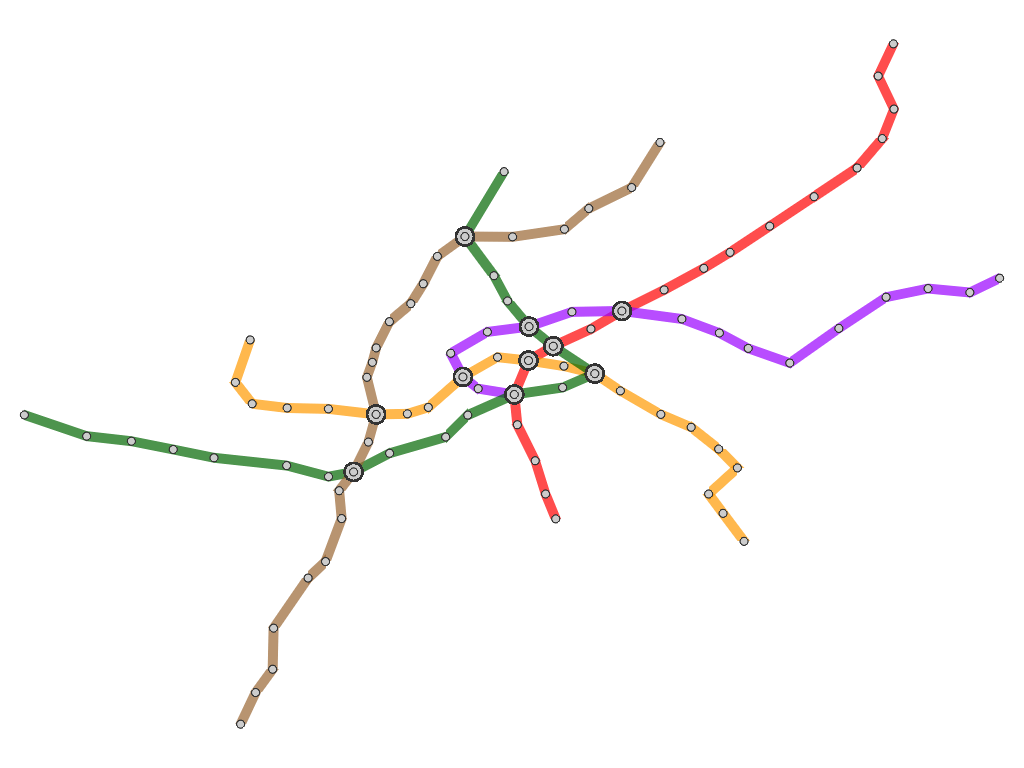
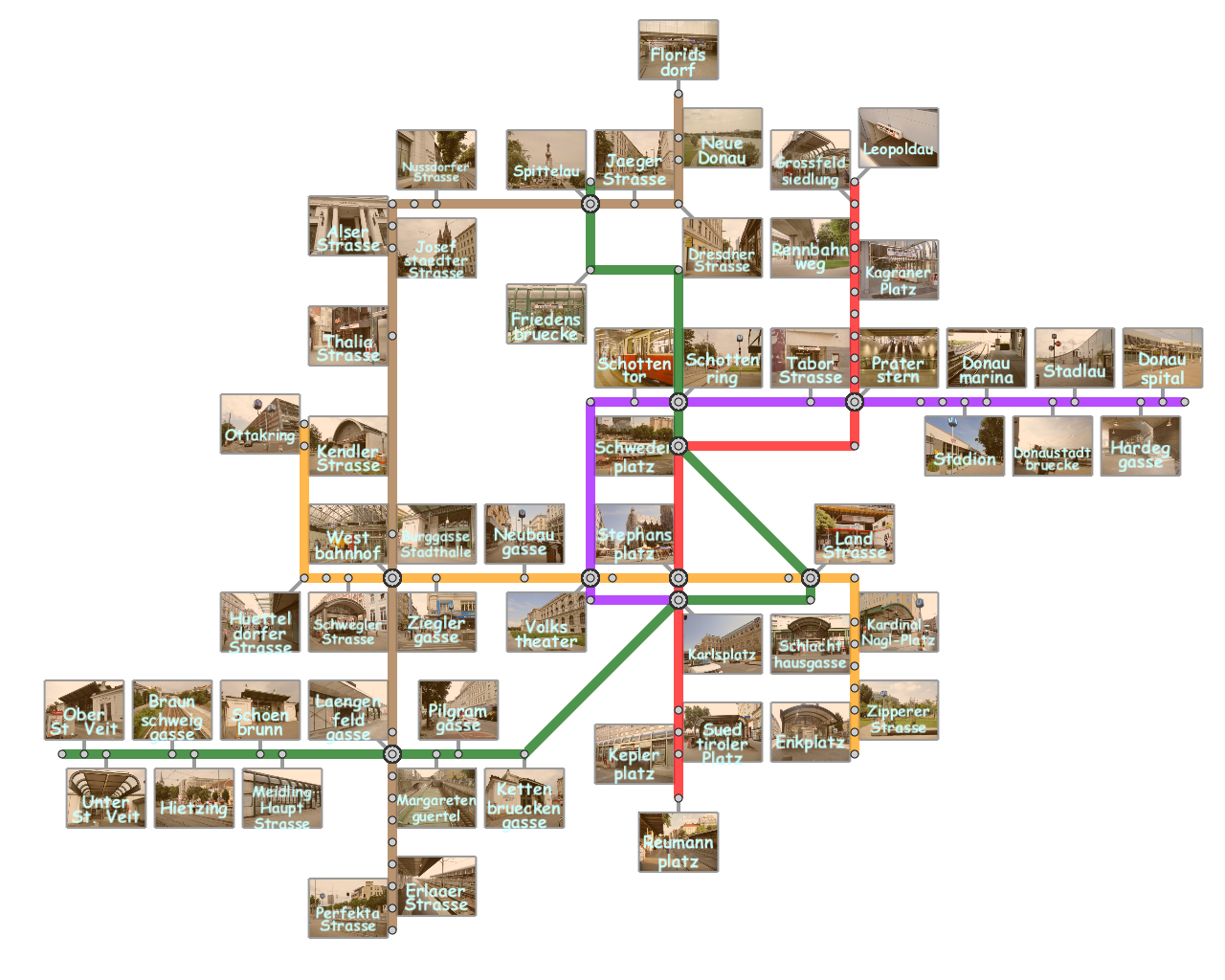
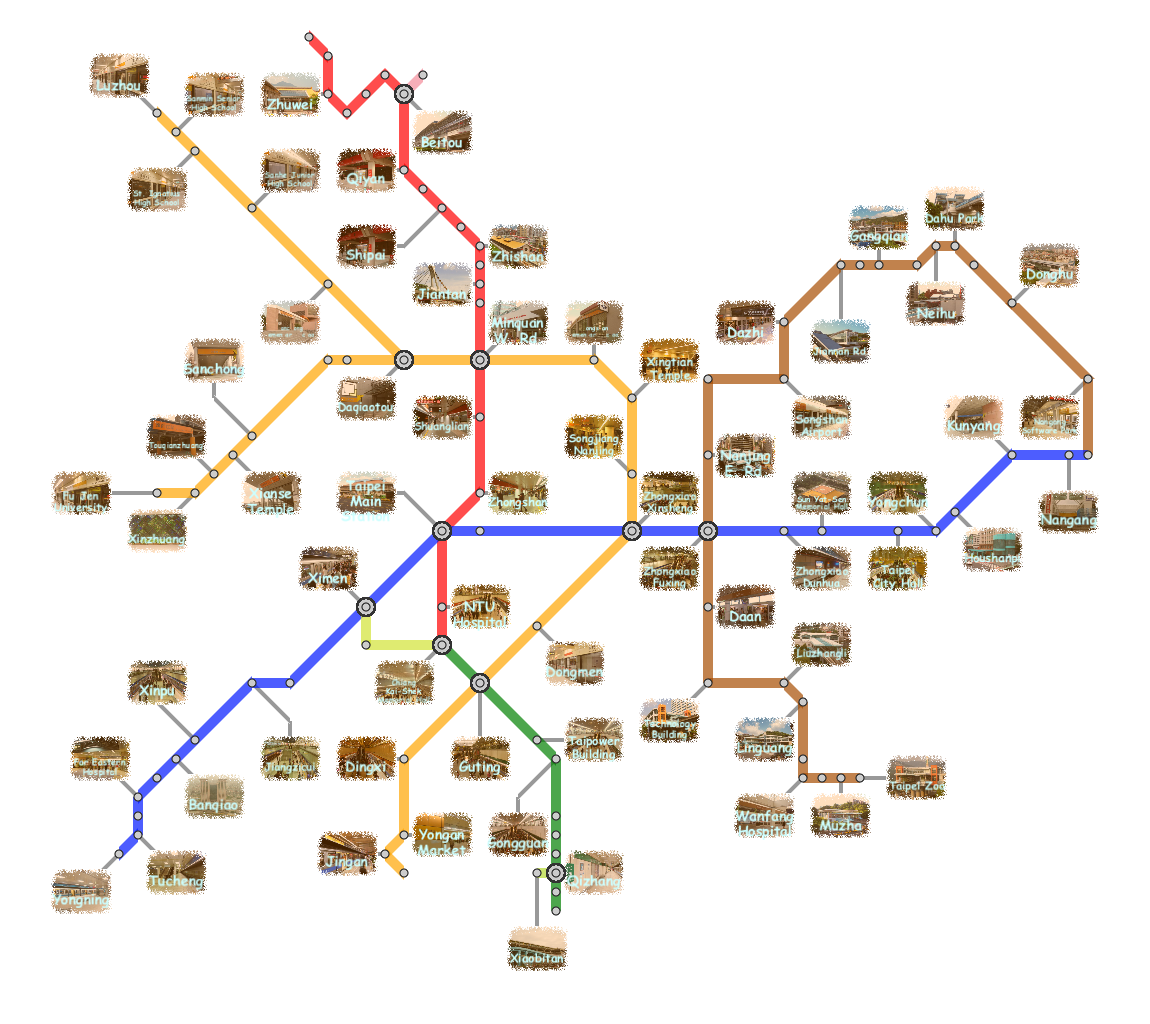
Results
Here, we present several results that are generated from our prototype system.
(You can click the thumbmail image for that of the original resolution.) |
Paper & VideoHsiang-Yun Wu, Shigeo Takahashi, Daichi Hirono, Masatoshi Arikawa, Chun-Cheng Lin, and Hsu-Chun Yen, Spatially Efficient Design of Annotated Metro Maps, Computer Graphics Forum (Proceedings of EuroVis 2013), Vol. 32, No. 3, pp. 261-270, 2013. Paper-preprint (PDF, 12.2MB), Video(MOV, 27.1MB) |