Abstract
Interpolating diffusion tensor fields is a key technique to visualize the
continuous behaviors of biological tissues such as nerves and muscle fibers.
However, this has been still a challenging task due to the difficulty
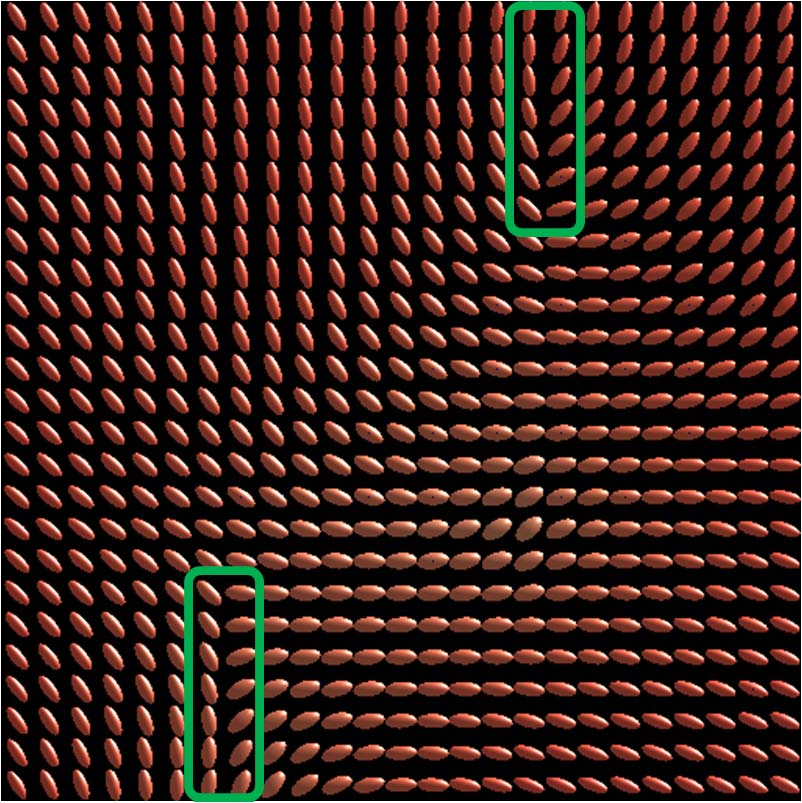
to handle possible degeneracy, which means the rotational inconsistency caused by degenerate
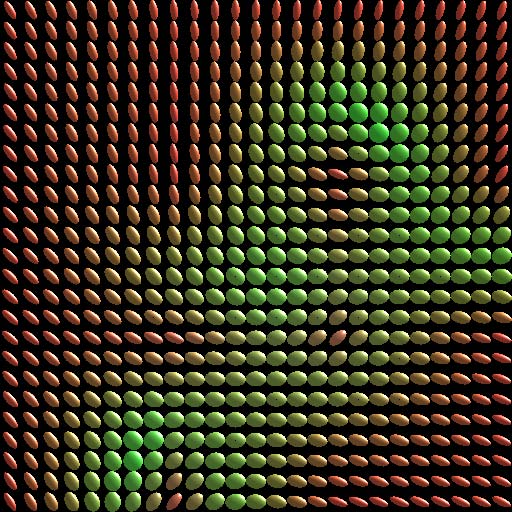
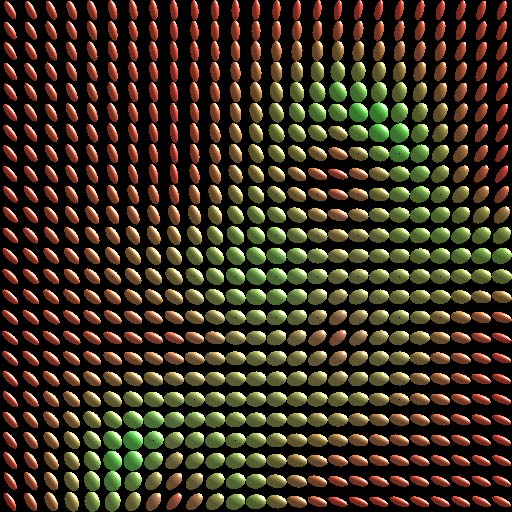
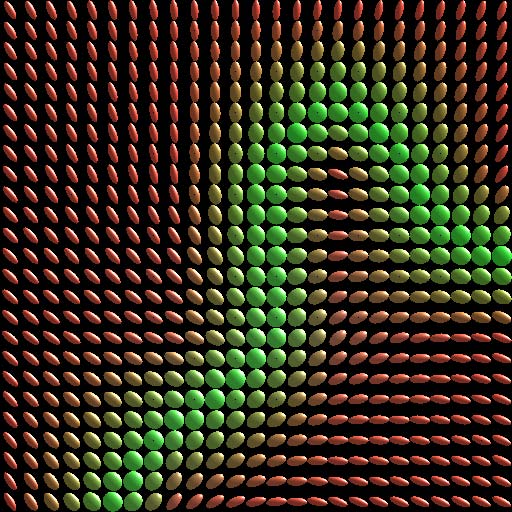
points. This paper presents an approach to interpolating 3D diffusion tensors in
2D planar domains by aggressively locating the possible degeneracy while fully
respecting the underlying transition of tensor anisotropy. The primary idea behind
this approach is to identify the degeneracy using minimum spanning tree-based
clustering algorithm, and resolve the degeneracy by optimizing the associated rotational transformations.
Degenerate lines are generated in this process to retain the smooth transitions of anisotropic features.
Comparisons with existing interpolation schemes will be also provided to demonstrate the technical advantages
of the proposed approach.
Paper
|