

Principal Investigators: Abderazek Ben Abdallah (PI), Khanh N. Dang (PI)
Driven by rapid advances in Artificial Intelligence, computer architecture, and high-fidelity sensor technologies, modern automobiles are undergoing a paradigm shift. Electric vehicles (EVs) and self-driving cars are evolving into sophisticated Automotive Edge Computing Platforms. These systems must concurrently execute a massive array of diverse applications, ranging from LiDAR-based environmental sensing and real-time navigation to occupant safety diagnostics.
Our research addresses the computational bottlenecks of these systems by developing application-specific intelligent microelectronics. We focus on low-latency, AI-powered hardware that supports lightweight communication protocols like Automotive Ethernet. By integrating real-time reliability and safety support at the hardware level, we ensure that these edge platforms can handle the rigorous demands of autonomous driving and Software-Defined Vehicles (SDVs).
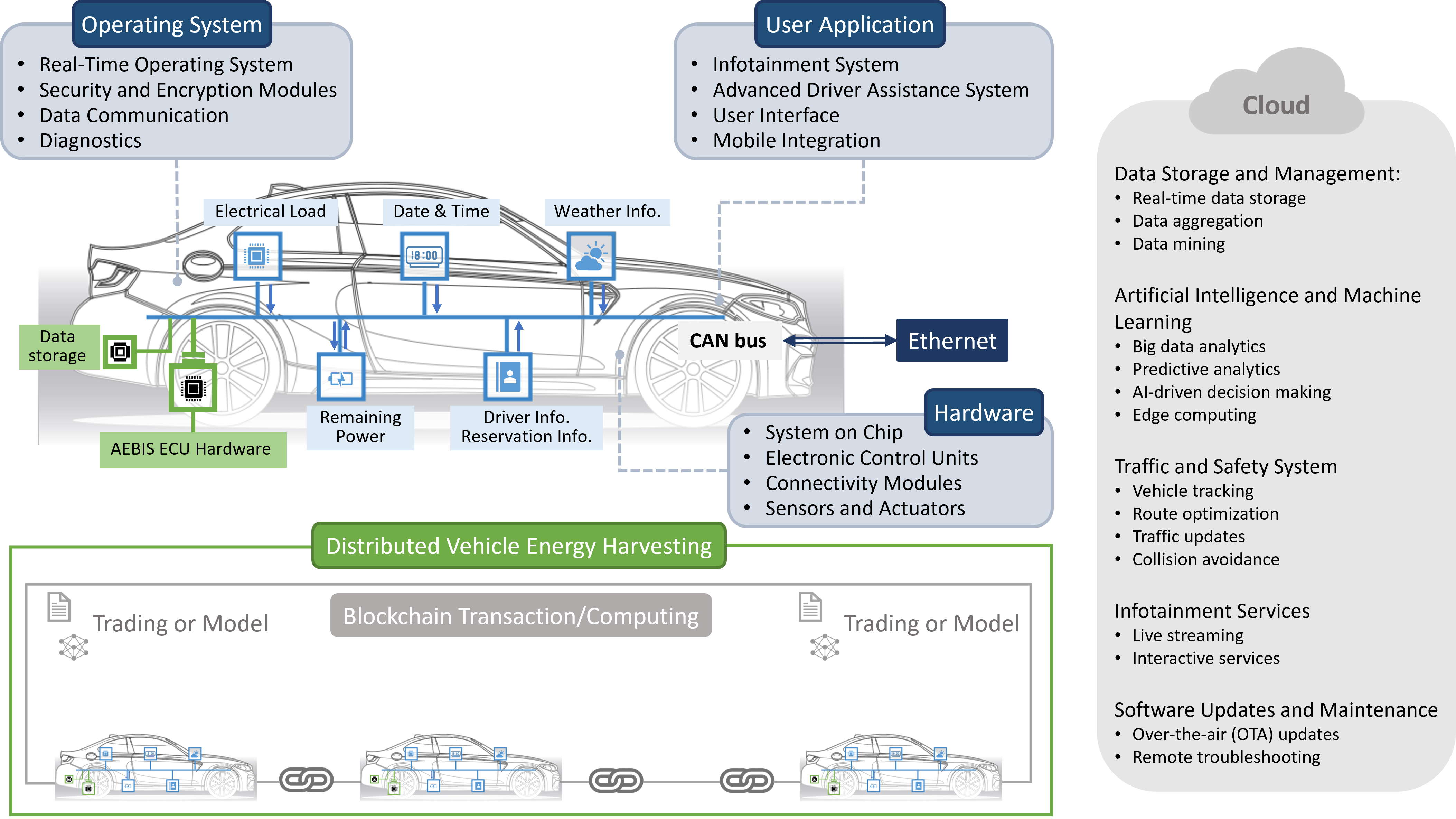
This project investigates the intersection of energy harvesting and intelligent management for next-generation electric vehicles. We develop AI-driven models that predict energy consumption based on driving patterns and road conditions. By dynamically managing harvested energy from regenerative sources, the system optimizes power delivery to the vehicle's edge computing units, ensuring maximum range without compromising the performance of safety-critical AI sensing systems.
Focused on the localized energy ecosystem, this research designs a secure, blockchain-based framework for energy trading between autonomous vehicles and campus infrastructure. This initiative utilizes IoT sensors and secure micro-transaction protocols to allow EVs to trade excess stored energy with building facilities. The "Trustworthy" component emphasizes cyber-physical security, ensuring that transactions are resilient against fraudulent data and network disruptions.
We study the development of lightweight communication protocols and hardware accelerators designed specifically for the automotive environment. This includes researching fail-operational support for in-vehicle networks and the design of chips that can withstand thermal and vibration stresses while providing high-throughput AI inference. Our goal is to bridge the gap between high-performance computing and the strict safety requirements of the automotive industry.