AI-powered EV Energy Harvesting and
Management[AI を活用した EV エネルギーの収集と管理]
A Virtual Power
Plant (VPP) is a network of distributed power generating
units, flexible power consumers, and storage systems. A
VPP bal ances the load on
the grid by allocating the power generated by different linked
units during peri ances the load on
the grid by allocating the power generated by different linked
units during peri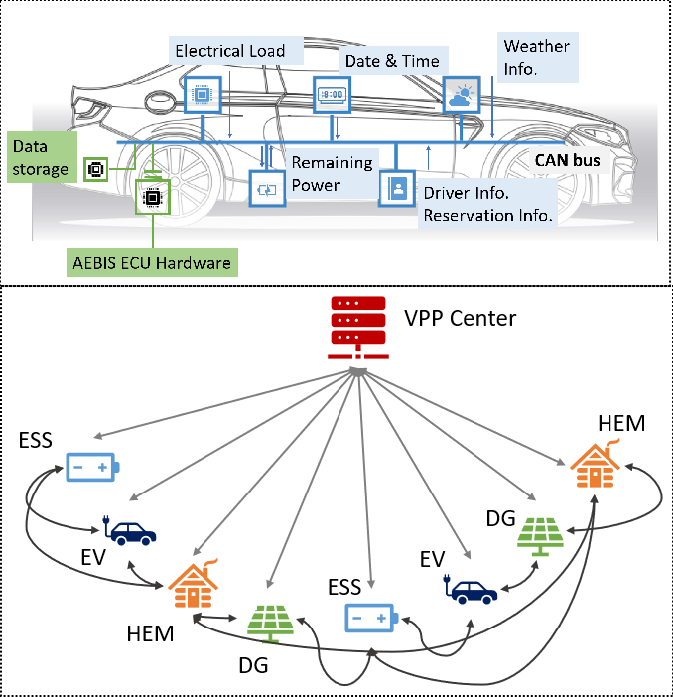 ods of peak load. Demand-side energy
equipment, such as Electric Vehicles ( ods of peak load. Demand-side energy
equipment, such as Electric Vehicles (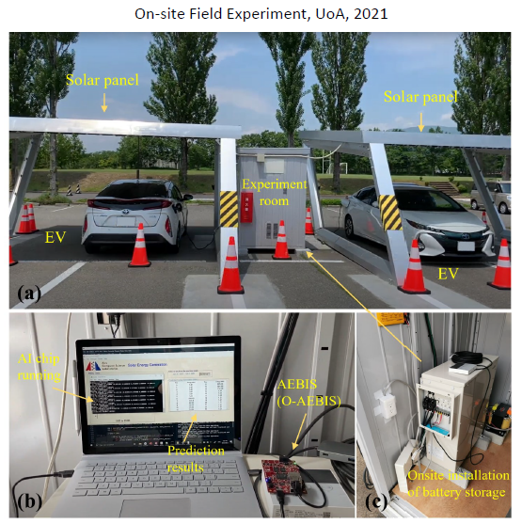 EVs) and mobile
robots, can also balance the energy supply-demand when
effectively deployed. However, fluctuation of the power
generated by the various power units makes the supply power
balance a challenging goal. Moreover, the communication
security between a VPP aggregator and end facilities is
critical and has not been carefully investigated. EVs) and mobile
robots, can also balance the energy supply-demand when
effectively deployed. However, fluctuation of the power
generated by the various power units makes the supply power
balance a challenging goal. Moreover, the communication
security between a VPP aggregator and end facilities is
critical and has not been carefully investigated.
In this project, we collaborate with Aizu
Computer Science Laboratories, Inc. and Banpu Japan to
develop an AI-enabled, block-chain-based Electric
Vehicle (EV) integration system for power management
in a smart grid platform based on EV and solar
carport. We have developed a low-power AI-chip
and various software tools for EV charge prediction,
in which the EV fleet is employed as a consumer and as
a supplier of electrical energy.
-
Z.
Wang, A. Ben Abdallah, ''A Robust
Multi-stage Power Consumption Prediction
Method in a Semi-decentralized
Network of Electric Vehicles,'' IEEE
Access, 2022. DOI:
10.1109/ACCESS.2022.3163455
A Virtual Power Plant (VPP) balances the load
on a power grid by allocating power generated
by various interconnected units during periods
of peak demand. In addition, demand-side
energy devices such as Electric Vehicles (EVs)
and mobile robots can also balance energy
supply and demand when effectively deployed.
However, the fluctuation of energy generated
by renewable resources makes balancing energy
supply a challenging goal. This paper proposes
a semi-decentralized robust network of
electric vehicles (NoEV) integration system
for power management in a smart grid platform.
The proposed approach integrates an aggregator
with EV fleets into a blockchain framework.
The EVs execute a multi-stage algorithm to
predict the power consumption based on a novel
federated learning algorithm named Federated
Learning for Qualified Local Model Selection
(FL-QLMS). From the evaluation results, the
proposed system requires 35% fewer
transactions in short intervals and
propagation delays than the previous
approaches and achieves better network
efficiency while maintaining a high level of
security. Moreover, NoEV achieves a 5.7% lower
root mean square error (RMSE) than the
conventional approach for power consumption
prediction, which is a significant
improvement. In addition, the FL-QLMS approach
outperforms state-of-the-art methods in terms
of robustness to client-side attacks. The
evaluation results also show that the
performance of FL-QLMS is not affected when
10% to 40% percent of the models are
manipulated.
-
Z.
Wang, M. Ogbodo, H. Huang, C. Qiu, M.
Hisada, A. Ben Abdallah, "AEBIS:
AI-Enabled Blockchain-based Electric Vehicle
Integration System for Power Management in
Smart Grid Platform," IEEE
Access, vol. 8, pp. 226409-226421, 2020,
doi:10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3044612.
 A
Virtual Power Plant (VPP) is a network of
distributed power generating units, flexible
power consumers, and storage systems. A VPP
balances the load on the grid by allocating
the power generated by different linked units
during periods of peak load. Demand-side
energy equipment, such as Electric Vehicles
(EVs) and mobile robots, can
also balance the energy supply-demand when
effectively deployed. However, fluctuation of
the power generated by the various power units
makes the supply power
balance a challenging goal. Moreover, the
communication security between a VPP
aggregator and end facilities is critical and
has not been carefully investigated. This
paper proposes an AI-enabled, blockchain-based
electric vehicle integration system, named
AEBIS for power management in a smart grid
platform. The system is based on an artificial
neural-network and federated learning
approaches for EV charge prediction, in which
the EV fleet is employed as a consumer and as
a supplier of electrical energy within a VPP
platform. The evaluation results show
that the proposed approach achieved high power
consumption forecast with R 2 score
of 0.938 in the conventional training
scenario. When applying a federated learning
approach, the accuracy decreased by only 1.7%.
Therefore, with the accurate prediction of
power consumption, the proposed system produces
reliable and timely service to supply extra
electricity from the vehicular network,
decreasing the power fluctuation level. Also,
the employment of AI-chip ensures a
cost-efficient performance. Moreover,
introducing blockchain technology in the
system further achieves a secure and
transparent service at the expense of an
acceptable memory and latency cost. A
Virtual Power Plant (VPP) is a network of
distributed power generating units, flexible
power consumers, and storage systems. A VPP
balances the load on the grid by allocating
the power generated by different linked units
during periods of peak load. Demand-side
energy equipment, such as Electric Vehicles
(EVs) and mobile robots, can
also balance the energy supply-demand when
effectively deployed. However, fluctuation of
the power generated by the various power units
makes the supply power
balance a challenging goal. Moreover, the
communication security between a VPP
aggregator and end facilities is critical and
has not been carefully investigated. This
paper proposes an AI-enabled, blockchain-based
electric vehicle integration system, named
AEBIS for power management in a smart grid
platform. The system is based on an artificial
neural-network and federated learning
approaches for EV charge prediction, in which
the EV fleet is employed as a consumer and as
a supplier of electrical energy within a VPP
platform. The evaluation results show
that the proposed approach achieved high power
consumption forecast with R 2 score
of 0.938 in the conventional training
scenario. When applying a federated learning
approach, the accuracy decreased by only 1.7%.
Therefore, with the accurate prediction of
power consumption, the proposed system produces
reliable and timely service to supply extra
electricity from the vehicular network,
decreasing the power fluctuation level. Also,
the employment of AI-chip ensures a
cost-efficient performance. Moreover,
introducing blockchain technology in the
system further achieves a secure and
transparent service at the expense of an
acceptable memory and latency cost.
-
Patent:
[特 許第6804072 号] (2020.12.04) Abderazek Ben
Abdallah, Masayuki Hisada, ''Virtual
Power Platform Control System [仮 想
発電所制 御システム]'', 特 願
2020-033678号 (2020.02.28)
-
Patent:
[特願2023-020162] Abderazek Ben Abdallah,Wang
Zhishang, Khanh N. Dang, Masayuki Hisada, ''EV
Power Consumption Prediction Method
and System for Power Management in Smart
Grid [ スマートグリッドにおける電力管理のためのEV消 費電力予測
方法とシステム ]'', 特願2023-020162
- Invited
lecture: イ
ンフォパワード・エネルギー概論/Introduction to Info-Powered
Energy: Grid Technology with ICT and EV/ICT・
EVによるグリッド技術, TUFS, Tokyo, June 6,
2024
===>AEBIS-2
Project (members
only)
**Tools: CAD: AutoCAD, SolidWorks||SW:
Simulink,
Altair HyperWorks,Vivado||Prototyping/Testing:
Autodesk Alias, FPGA
産業界から当研究室との共同研究にご興味が ございましたら、ベ ン
アブダラ アブデラゼク教授(Eメール:benab@u-aizu.ac.jp)までご連絡ください。
|


 ances the load on
the grid by allocating the power generated by different linked
units during peri
ances the load on
the grid by allocating the power generated by different linked
units during peri ods of peak load. Demand-side energy
equipment, such as Electric Vehicles (
ods of peak load. Demand-side energy
equipment, such as Electric Vehicles ( EVs) and mobile
robots, can also balance the energy supply-demand when
effectively deployed. However, fluctuation of the power
generated by the various power units makes the supply power
balance a challenging goal. Moreover, the communication
security between a VPP aggregator and end facilities is
critical and has not been carefully investigated.
EVs) and mobile
robots, can also balance the energy supply-demand when
effectively deployed. However, fluctuation of the power
generated by the various power units makes the supply power
balance a challenging goal. Moreover, the communication
security between a VPP aggregator and end facilities is
critical and has not been carefully investigated.