Trustworthy Campus Energy Trading System
Energy trading policies are revolutionizing the efforts and policies geared toward addressing global carbon emissions and protecting the environment. Smart grids and electric vehicles (EVs) are energy-saving tools for efficient power management.
Although EVs can act as both energy consumers and suppliers, the effort required to balance the energy supply and demand in typical centralized trading systems inevitably reduces trading reliability. Another challenge is distributing EVs’ energy rationally to achieve better demand response and energy utilization.
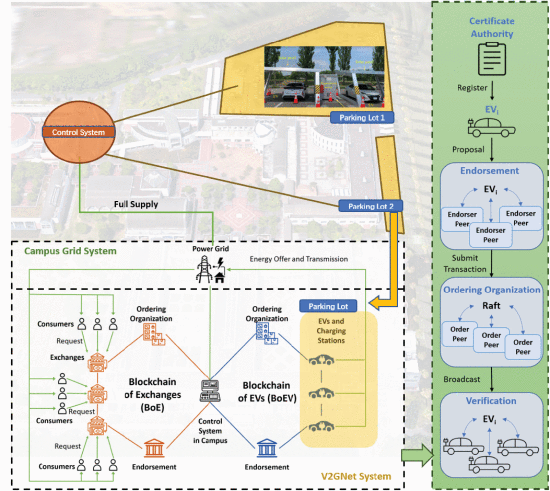
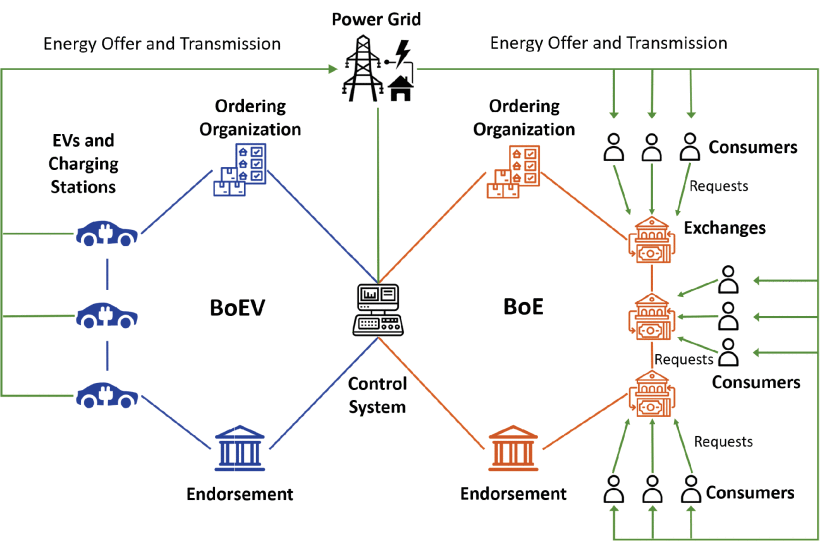
This project investigates a secure blockchain-based energy trading system using the vehicle-to-grid (V2G) network. The system combines a blockchain of energy exchanges and a blockchain of EVs with the distinct transmission of energy requests and offers.
Key Publications & Research
A decentralized intelligent V2G system (V2GFTN) achieving efficient and robust energy trading. Demonstrated 1.9x higher demand fill rate than state-of-the-art V2G approaches.
Proposes V2GNet, managing markets securely via a dual-blockchain structure. Reduces energy loss by 30% during malicious consumer attacks.
Patents & Resources
- Patent: [特願2022-022472] Abderazek Ben Abdallah, Wang Zhishang, Masayuki Hisada, "An electricity trading system and an electricity trading method [電力取引システム及び電力取引方法に関する]"
- UoA Energy-Related Research Intro [会津大学エネルギー関係研究紹介]
- AI-enabled Vending Machine with Off-grid Energy Harvesting
産業界から当研究室との共同研究にご興味がございましたら、
ベン アブダラ アブデラゼク教授(Eメール:benab@u-aizu.ac.jp)までご連絡ください。